In the modern world, one of the fundamental aspects of health care is health insurance which most families require in order to cater for their health needs. Out of many several kinds of health insurance programs in the market, three of them namely: HMO, PPO, and EPO plans are some of the most commonly used by people. All of them have their pros and cons and this might confuse people wanting to get coverage. The need this guide fulfills is to explain these plans in detail so that a reader is able to select one as per his individual circumstances.
Which of HMO, PPO, and EPO is more favorable for consumers in terms of cost and coverage options?
The first step to achieving that is to comprehend the differences among the plans.
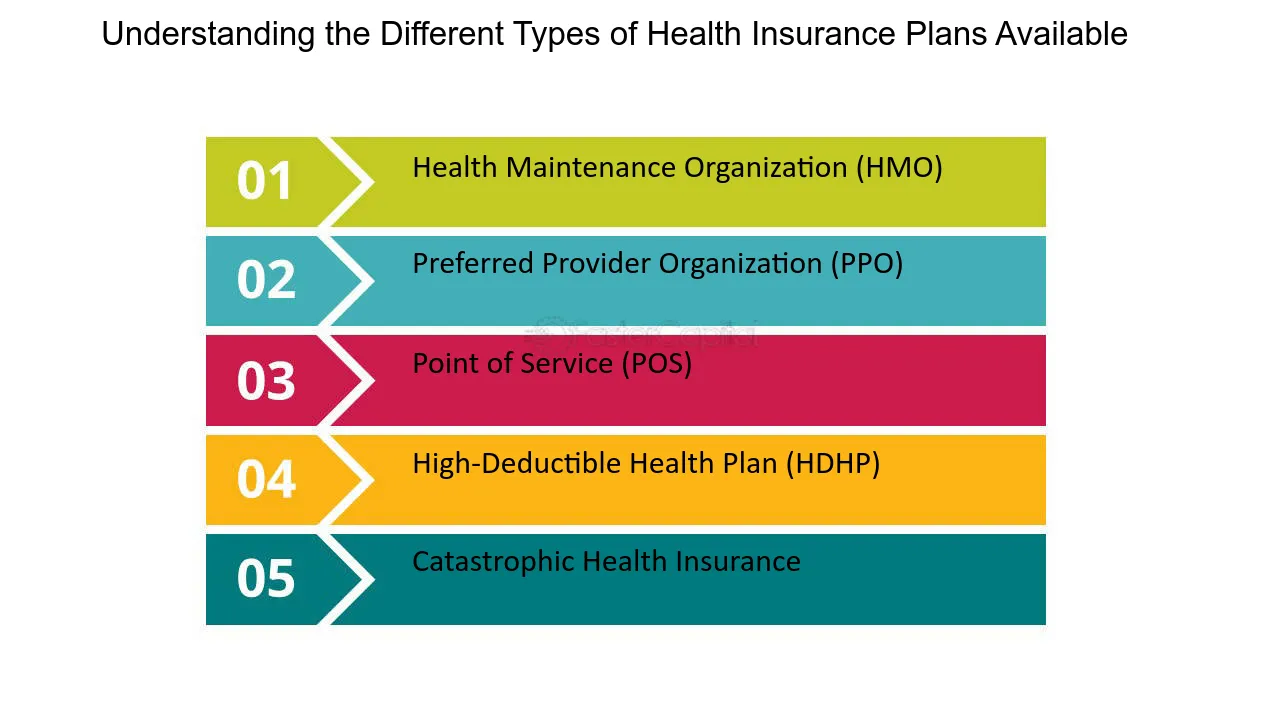
HMO (Health Maintenance Organization)
HMO plans focus on prevention of illnesses and more often than not require their members to have a specific primary care physician (PCP).
PCP stands for Primary Care Physician: someone who acts as your healthcare’s conductor.
Referrals Required: To go to a specialist, you must obtain a referral from your primary care physician.
Network Restrictions: There are limitations on where you can receive care services unless it is an emergency.
Lower Costs: The vast majority of premium and out of pocket expenses are low.
PPO (Preferred Provider Organization)
PPO plans allow for greater flexibility along with a wide variety of providers to choose from.
Referrals Not Required: Specialist appointments can be made without referral.
Network Flexibility: Permits the use of both in-network and out-of-network providers.
Increased Costs: Premiums as well as out-of-pocket expenses tend to be quite high.
Best suited for those who travel often. Offers valuable benefits when traveling outside the local area.
EPO (Exclusive Provider Organization)
EPO is an intermediate form between HMO and PPO plans.
In-Network Only: The coverage is limited to within the network only.
No Referrals Required: You may visit specialists without the need for a primary care physician.
Cost-Effective: Cost is balanced with the flexibility, providing good quality at a reasonable price.
What are the 3 Guidelines that Stand Out in Distinction between HMO and PPO Insurance?
HMO and PPO plans differ in three primary areas:
Provider Networks: Care in HMO plans is provided by in-network providers only, whereas in PPO plans outside the network is also available though at higher costs.
Referrals: HMO members need a referral from their PCP to see a specialist. PPO members do not.
Costs: HMO members tend to pay lower costs in premiums and out-of-pocket expenses whereas members that utilize PPO plans pay higher costs but are able to enjoy more flexibility.
| Comparison | HMO | PPO |
|---|---|---|
| Network Flexibility | In-network only | In- and out-of-network |
| Referrals Needed | Yes | No |
| Costs | Lower premiums and out-of-pocket | Higher premiums and out-of-pocket |
Which Health Insurance Plans Are in Most Use?
In the United States, there are two mainstream plans:
HMO Plans: Economical and oriented to dealer and intensive preventive measures.
PPO Plans: Its flexibility in choosing providers and ease of consulting a specialist makes the Plan preferred.
These alternatives address most health coverage requirements, and thus these plans are common features in insurance offerings.
What’s United Healthcare PPO?
It’s a health insurance plan within the Unified Healthcare offering a range of plans from UnitedHealthcare, a major insurer in the United States.
Wide Network: Offers a wide range of healthcare providers.
Flexible Coverage: Provides coverage for out-of-network providers, but at a premium rate.
Comprehensive Benefits: Covers preventive services, specialty care, and chronic care management.
For most active persons who would like flexibility and an extensive network, United Healthcare PPO plans are ideal.
Things that Should Guide You as You Choose a Plan
1. Budget: You would do well with the HMO plans if you did not want to pay high premium rates. Individuals willing to pay much to have a variety of providers may go for the PPO and EPO plans.
2. Healthcare Needs: You may consider PPO or EPO plans if you move around a lot or prefer certain specialists.
3. Favorite Physicians and Health Facilities: Always check if the health provider you want is within the plan’s network so that you don’t incur unanticipated expenses.
4. Long-Term Illness or Special Treatment Needs: PPO plans tend to be more useful for people who have a chronic disease or those who require more specialized treatment.
A Comparison of HMO, PPO, and EPO Features:
| Feature | HMO | PPO | EPO |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCP Requirement | Yes, | No | No |
| Specialist Referrals | Required | Not Required | Not Required |
| Network Flexibility | Limited to in-network | Includes out-of-network | Limited to in-network |
| Costs | Low premiums, low out-of-pocket | High premiums, higher out-of-pocket | Moderate premiums, moderate costs |